
Google Bard Just Got Significant Updates
Google’s innovative AI model, Bard, is undergoing two significant updates that debuted yesterday, as announced by Jack Krawczyk, Product Lead for Bard, and Amarnag Subramanya, Vice President of Engineering.
These improvements are aimed at enhancing Bard’s abilities to handle mathematical tasks, coding questions, and string manipulation. Moreover, Bard now features an ‘export to Google Sheets’ function, enabling users to create and export tables directly into Sheets.
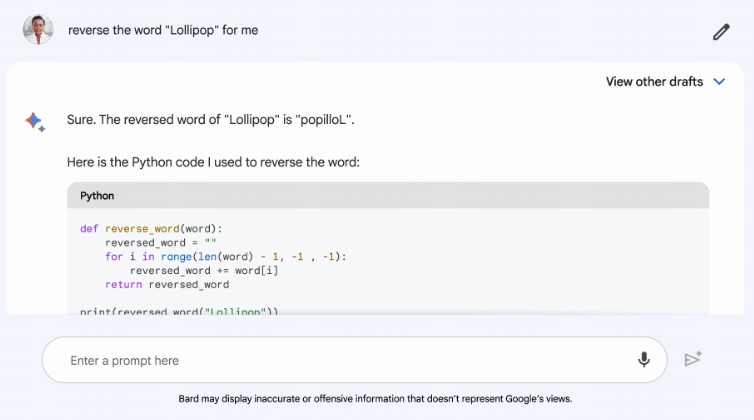
One of the key enhancements involves the introduction of a technique known as “implicit code execution,” allowing Bard to detect computational prompts and execute code in the background. This feature will help Bard to respond more accurately to complex prompts, such as calculating prime factors or reversing strings.
The aim of these improvements is to extend Bard’s logic and reasoning capabilities, which have been a challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs) in the past. LLMs, including Bard, function much like prediction engines, generating responses by predicting subsequent words based on a given prompt. While LLMs perform exceptionally well in language and creative tasks, they often struggle with reasoning and mathematical tasks.
To resolve this, Google has drawn inspiration from the psychological constructs of System 1 and System 2 thinking, a concept presented by psychologist Daniel Kahneman in his book “Thinking, Fast and Slow”. System 1 involves intuitive, fast, and effortless thinking, while System 2 is slow, deliberate, and effortful.
The new method combines both modes of thinking to enhance Bard’s responses. Through “implicit code execution,” Bard identifies prompts that would benefit from logical code execution and generates a response that is more accurate. This method has increased the accuracy of Bard’s responses to computation-based problems by about 30% in internal testing, making Bard more efficient and helpful than ever before.
Google shows examples of Bard answering the question, “reverse the word ‘Lollipop’ for me” and the chatbot types it out, but also shares the Python code used to come up with the answer.
However, Google acknowledges that Bard might not always get it right. Bard may fail to generate the required code, produce incorrect code, or not include the executed code in its response. Despite these challenges, these updates mark a crucial step forward in enhancing Bard’s structured, logic-driven capabilities.
Google Bard is not available in Canada just yet, despite expanding to over 180 countries and territories last month. The reason for not including Canada? Google says it is taking its time to expand Bard.
How to use Bard in Canada? Just use a VPN service and change your location to the U.S. and it will work like a charm.

